FDM – printing process
The FDM (=Fused Deposition Modeling) process, also known as the melt layering or nozzle melting process, is based on the melting and subsequent layer-by-layer application of a plastic (usually ABS or PLA). In FDM printing, the plastic to be processed is fed to an extruder in filament or rod form, where it is melted and applied to a (usually heated) print bed using a hotend and nozzle in accordance with the structure defined in the CAD files. Depending on the model of the FDM printer, the nozzle, print bed or both are movable.
The FDM technology, also known as FLM (=Fused Layer Modeling) or FFF (=Fused Filament Fabrication), was developed by Scott Crump in 1988 and is one of the most widely used 3D printing processes today.
We source our materials and raw materials exclusively from renowned manufacturers such as extrudr, spectrum and formlabs to ensure consistently high quality.
DuraPro ABS
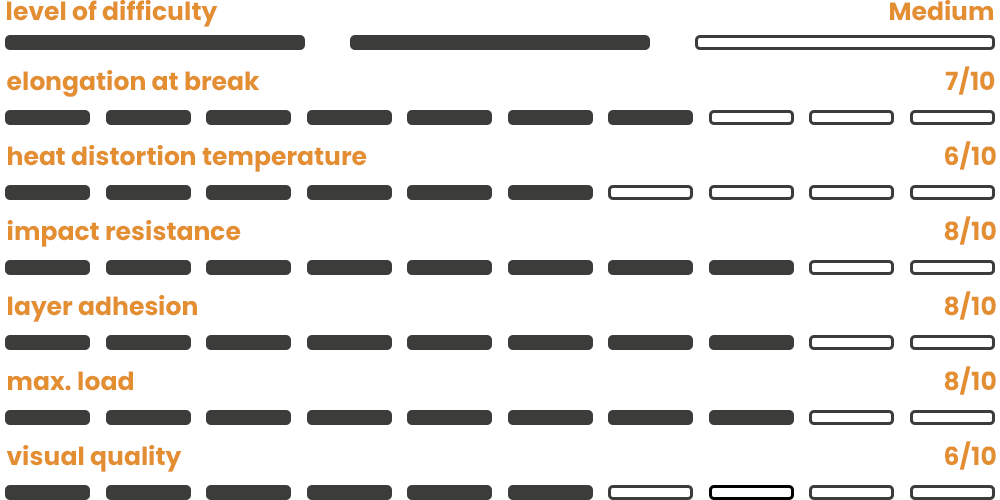
DuraPro ABS has been specially developed for industrial applications and is characterized by its high process reliability. It is ideal for the manufacture of components subject to high mechanical loads. The material is electrically insulating. DuraPro ABS is optimized for good layer adhesion, thermal stability, improved flow properties and low warpage. The raw material is approved in accordance with REACH, RoHS and FDA standards.
- For industrial applications
- Flame retardant according to UL 94 HB
- Electrically insulating
- High mechanical strength
- Low shrinkage and deformation
- Excellent layer and bed adhesion

ASA +
ASA+ was specially developed for industrial applications and is characterized by its high UV and weather resistance. It is therefore particularly suitable for use in the automotive sector and outdoors. The material is flame-retardant in accordance with UL94 HB. ASA+ has been optimized for the FFF/FDM process so that the material has good layer adhesion, thermal stability, improved flow properties and low warpage.
- UV and weather resistant
- Matt surface
- High mechanical strength
- Good layer and bed adhesion
- Low warpage

GreenTec Pro
GreenTEC Pro comes from the BIO Performance range and has been specially developed for ultra-high-performance applications. The material has a heat deflection temperature of 160°C (VST A – 4mm wall thickness) and is optimized for high rigidity and flexural strength. The material offers a high-quality, semi-matt appearance. GreenTEC Pro is the ecologically harmless alternative to conventional industrial materials, consists of 100% renewable raw materials and is biodegradable in accordance with DIN EN ISO 14855. The raw material also has food approval (FDA).
- 100% sustainable and oil-free
- Silk-matt appearance
- Biodegradable (DIN EN ISO 14855)
- Heat resistance up to 160°C VICAT A / 115°C HDT/B*
- Impact strength

PETG
Polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) is one of the best-known thermoplastic polymers in the world. Extrudr PETG has been developed for a wide range of applications where a balance between mechanical and optical material properties is particularly important. The low-shrinkage technology ensures that the material can be processed at low temperatures to save energy and thus with relatively little warping. The raw material is certified in accordance with FDA, REACH and RoHS standards.
- Good mechanical properties
- High chemical resistance
- Low warpage
- Low shrinkage
- Recyclable
- Low shrinkage technology

PLA NX2
PLA NX2 MATT & TOUGH is a new generation of PLA with improved mechanical properties compared to normal PLA. The optimized surface offers a detailed print quality. It is also suitable for mechanically stressed parts due to its impact resistance and higher flexibility.
- Matt surface
- Mechanically resilient
- CO2-neutral
- Good tensile strength
- Improved UV resistance
- Complies with FDA, RoHS and safety regulations for toys

TPU Flex Hard
TPU Flex Hard was developed for use in FDM/FFF 3D printing and offers high flexibility with its stretchability of up to 480 %. It is characterized by excellent quality, resistance to chemicals and temperature resistance up to 140 °C, which makes it suitable for many industrial applications. This material also meets the requirements of REACH and RoHS regulations.
- Highly resistant to impact and breakage
- Contains no halogen
- Free from silicone, plasticizers and oils
- Has a Shore hardness of D58
- Resistant to UV radiation
- Provides excellent adhesion between the print layers

SLA – Stereolithography
Stereolithography, also known as SLA printing, was invented back in 1983 and can therefore be considered the “mother of all 3D printing processes”. The starting point for SLA printing is a tank filled with a liquid photopolymer (epoxy resin), the most important property of which is that it solidifies after a certain exposure time. A laser is then used to project the individual layers of the model into the plastic, whereby the movable print bed is pulled down until the model is finished. Finally, the hardened object is removed from the bath and usually exposed in a separate exposure chamber until it is completely hardened.
Technical materials to be mentioned:
Durable Resin:
- Durable Resin is the most pliable, impact resistant and slip resistant material in our functional SLA product family of Tough and Durable Resins. Choose Durable Resin for malleable parts and low-friction assemblies.

Tough 2000 Resin:
Tough 2000 Resin is the strongest and stiffest material in SLA’s functional family of Tough and Durable Resins. Choose Tough 2000 Resin for prototyping strong and durable parts that should not bend easily.
SLS – Selective laser sintering
- In industrial 3D printing, selective laser sintering (SLS printing) is currently by far the most frequently used 3D printing process, as it enables long-term stable models at affordable prices. In the SLS process, the starting material in powder form is fused with pinpoint accuracy using a laser beam and built up into a fracture-resistant model.
MJF – MultiJet Fusion
- In MultiJet Fusion (MJF), also known as MultiJet Fusion or PolyJet printing, a photopolymer (= light-sensitive) plastic is applied to a platform through several nozzles (hence the name) and immediately cured by a light source integrated in the print head. The MJF process can therefore be considered a kind of mixture of stereolithography and FDM printing and enables very detailed models.
PA
- PA stands for polyamide. The various polyamides, including nylon, are processed into fibers in large quantities. Nylon plastic is characterized by a number of outstanding properties, including high wear resistance, a good coefficient of friction and excellent temperature resistance and impact strength. These properties make it one of the most important engineering plastics.

